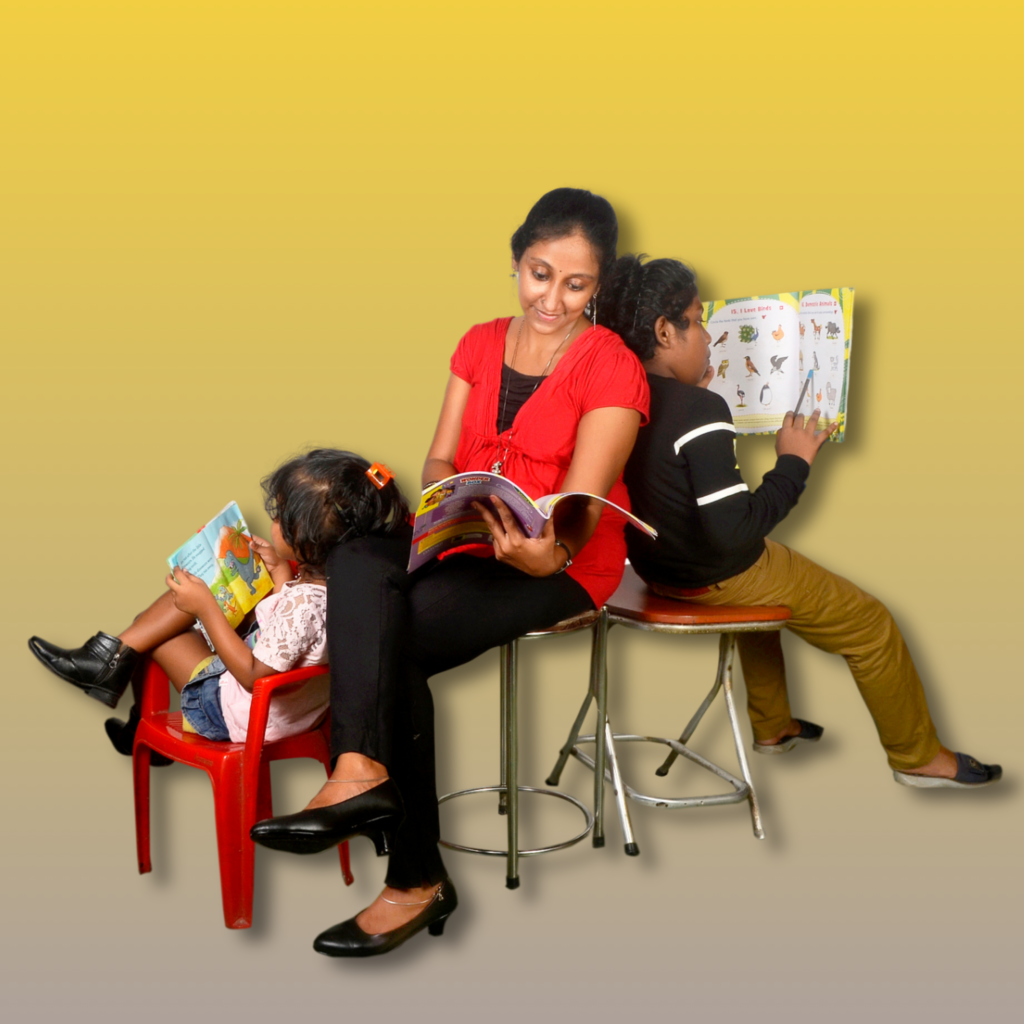

Welcome to Eduparenting Hub, where we are dedicated to unlocking the hidden genius in every child. At Eduparenting Hub, we believe that every child is born with unique talents, skills, and potential. Our mission is to help parents, educators, and children understand and harness these innate abilities through the power of Dermatoglyphics Multiple Intelligence Test (DMIT).


Our vision is to revolutionize the way children are nurtured and educated by providing personalized insights into their intellectual and emotional strengths. Through our DMIT services, we empower parents and teachers with knowledge that can guide children to their fullest potential, helping them succeed in school, life, and beyond.
DMIT is a scientifically backed test that analyzes the patterns of a child’s fingerprints to provide a deep understanding of their multiple intelligences, personality traits, learning styles, and emotional strengths. The test reveals the natural talents and cognitive abilities of a child, enabling educators and parents to tailor learning approaches that align with each child’s unique abilities.

Our team is comprised of experienced professionals who specialize in child development, psychology, and education. We ensure every test result is accurately interpreted to offer the most valuable insights for your child.
We focus not just on academics but on the overall development of the child, helping them excel in various areas such as creativity, social intelligence, leadership, and emotional well-being.
The DMIT provides a tailor-made roadmap that highlights your child’s strengths, learning preferences, and areas of improvement. This helps you make informed decisions in guiding your child’s education and personal growth.
Our services are based on extensive research in genetics, neuroscience, and psychology, ensuring that the information we provide is reliable and backed by science.
We work with parents and schools to develop learning strategies that suit the child’s strengths, improving their academic performance and overall development.
By identifying natural abilities early on, we help children pursue activities that align with their interests and innate talents, whether in the arts, sports, science, or leadership.
As children grow, their strengths and talents guide their career paths. We provide insights that can help direct children toward fulfilling and successful futures.
We offer advice and resources for parents, helping them understand their child’s needs and how to support their growth effectively.

At Eduparenting Hub, we are committed to fostering a positive, nurturing environment where children can explore their potential and develop into confident, intelligent individuals. We believe that every child has the ability to achieve greatness with the right guidance and support.
Join us in our mission to uncover the genius within every child and create a brighter, more personalized future for their growth and success.
The science of fingerprints, initially used for personal identification, is known as dactyloscopy. This method became widely recognized in forensic science, particularly within criminal investigations. However, the development of dermatoglyphics as a science focusing on the study of skin patterns, particularly fingerprints, was pioneered by Dr. Harold Cummins, who introduced it as a method to study the relationship between fingerprint patterns and human characteristics.
The term dermatoglyphics is derived from Greek, where derma means skin and glyph means carving, referring to the unique patterns found on the skin, primarily on the fingertips, palms, and soles. These patterns were linked to genetic formation, specifically the development of brain cells.
were among the early researchers who observed and documented the relationship between fingerprints and human traits.
published a book, Your Life in Your Hands, where he discussed the potential to analyze hand patterns and their link to psychological and physical traits.
concluded that fingerprints could reflect a person’s characteristics and psychological aspects.
The concept of using dermatoglyphics to measure intelligence took a significant step forward with the work of Zhai Guijun, a Chinese scientist who, starting in 1988, conducted extensive research on Multivariate Intelligence Measurement through Dermatoglyphic Identification. This method, developed over nearly two decades, is based on the idea that fingerprints can provide a reliable and accurate assessment of human intelligence and personality. Zhai’s research included sampling over 40,000 people and led to the development of a systematic method for measuring intelligence through fingerprint patterns.
This method, which received recognition from various scientific bodies, such as the Henan Academy of Sciences and China Psychological Society, posits that fingerprints reflect brain activity and genetic makeup, thus allowing for the measurement of intelligence. According to Zhai, dermatoglyphics is an efficient way to evaluate individuals’ cognitive abilities, and it can be used for educational and career guidance to align people’s talents with appropriate fields
